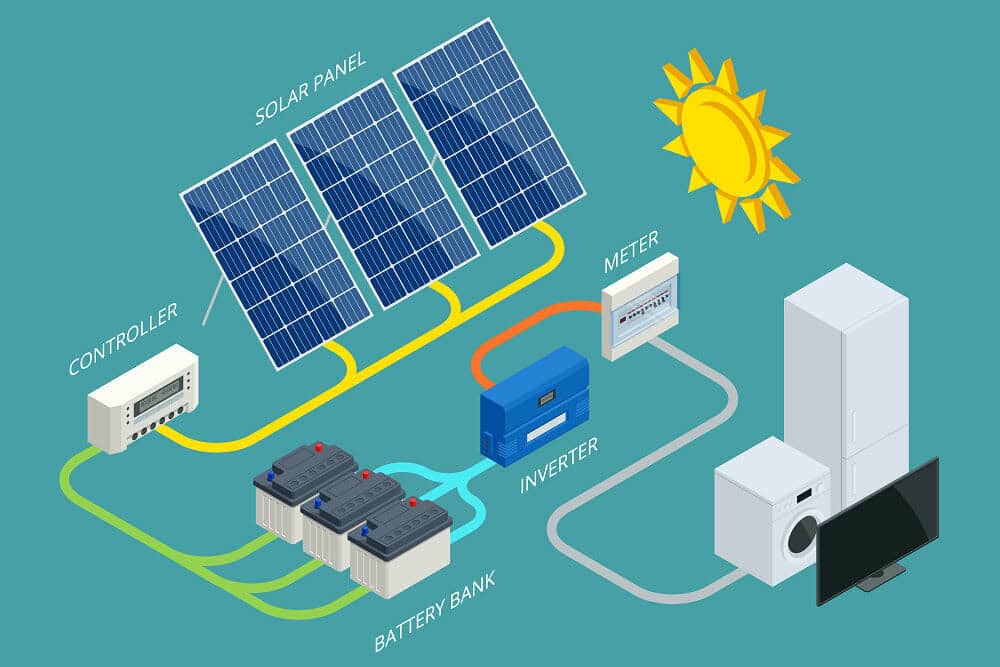
In recent years, solar energy has emerged as one of the most popular and sustainable sources of power. With the increasing need for renewable energy solutions and the push for reducing carbon footprints, solar power has become essential for homes, businesses, and industries. However, a key challenge with solar energy is its intermittency — the sun doesn’t always shine when we need power the most. This is where solar energy storage systems come into play, enabling us to store excess solar energy generated during the day and use it when the sun isn’t shining. In this blog post, we will dive into the types of solar energy storage systems and their efficiency, helping you understand how to make the most of solar power for your needs.
What is a Solar Energy Storage System?
A solar energy storage system allows the excess electricity generated by solar panels during the day to be stored for later use. These systems are designed to store the energy in various types of batteries or other storage technologies. This stored energy can then be used at night, during cloudy days, or in times of high energy demand, ensuring a continuous and reliable energy supply.
Types of Solar Energy Storage Systems
There are several types of solar energy storage systems available, each with its advantages and limitations. The most common types are:
1. Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries are currently the most popular and widely used energy storage technology for solar systems. These batteries are known for their high energy density, longer lifespan, and fast charging capabilities.
Advantages:
- Long lifespan (typically 10-15 years)
- High efficiency (90% or more)
- Compact and lightweight design
- Low maintenance
Disadvantages:
- Higher initial cost
- Requires careful management to avoid overcharging or overheating
2. Lead-Acid Batteries
Lead-acid batteries are one of the oldest and most cost-effective types of energy storage. These batteries are commonly used in off-grid solar systems but are also used in grid-connected systems.
Advantages:
- Lower initial cost compared to Li-ion batteries
- Widely available and easy to install
Disadvantages:
- Shorter lifespan (typically 3-5 years)
- Lower energy density
- Require regular maintenance (e.g., checking water levels)
3. Saltwater Batteries
Saltwater batteries are an emerging technology that uses a saltwater solution as the electrolyte. These batteries are non-toxic, environmentally friendly, and safer than lithium-ion batteries.
Advantages:
- Eco-friendly and non-toxic
- Long lifespan
- Safe with no risk of fire or explosion
Disadvantages:
- Lower energy density compared to lithium-ion and lead-acid batteries
- Still a relatively new technology with limited availability
4. Flow Batteries
Flow batteries store energy in liquid electrolyte solutions that flow through a cell stack to generate power. They are scalable and suitable for both residential and industrial applications.
Advantages:
- Long lifespan (up to 20 years)
- Scalable and can store large amounts of energy
- Can be recharged quickly without degradation
Disadvantages:
- Expensive
- Bulky and require more space
- Lower energy density than lithium-ion batteries
5. Hydrogen Storage
Hydrogen storage involves using excess solar energy to produce hydrogen through electrolysis, which can then be stored and converted back into electricity when needed. This technology is still in development but shows promise for large-scale energy storage.
Advantages:
- High energy capacity
- Can be used for long-term energy storage
Disadvantages:
- High cost and complex infrastructure
- Efficiency losses during conversion
Efficiency of Solar Energy Storage Systems
The efficiency of solar energy storage systems is an important consideration when choosing a system for your needs. Efficiency refers to the amount of energy stored that can be retrieved and used effectively.
- Round-trip Efficiency: This is the ratio of energy retrieved from the storage system compared to the energy put into it. For example, if you put 1 kWh of energy into the battery and only retrieve 0.9 kWh, the round-trip efficiency is 90%.
- Lithium-ion batteries typically have round-trip efficiencies of around 90-95%.
- Lead-acid batteries have lower round-trip efficiencies, typically around 75-85%.
- Flow batteries generally offer efficiencies between 65-85%.
- Saltwater and hydrogen storage can have lower efficiencies, with hydrogen particularly losing a significant amount of energy during conversion.
- Energy Density: This measures how much energy a storage system can hold relative to its size or weight. Lithium-ion batteries have the highest energy density, making them ideal for residential and commercial use where space is limited.
- Lifespan: The longer a storage system lasts, the more cost-effective it becomes in the long run. Lithium-ion and flow batteries have the longest lifespans, typically ranging from 10 to 20 years, whereas lead-acid batteries may only last 3-5 years.
- Cost vs. Efficiency: While more efficient systems like lithium-ion batteries offer higher initial costs, they provide better value over time due to their efficiency and longer lifespan. Lead-acid batteries, while cheaper upfront, may incur higher long-term costs due to their shorter lifespan and lower efficiency.
Conclusion
Solar energy storage systems are a crucial component of a solar power setup, ensuring that excess energy generated during the day can be stored and used when needed. The choice of energy storage system depends on various factors such as cost, space, lifespan, and efficiency. Lithium-ion batteries offer high efficiency and a long lifespan, making them the most popular choice for most residential and commercial solar systems. However, other options like lead-acid, flow, and saltwater batteries provide alternatives for specific needs or budgets. Understanding the different types of storage systems and their efficiencies will help you make an informed decision about which system is best suited for your solar energy goals. Whether you’re looking to reduce your electricity bills, ensure energy independence, or contribute to a more sustainable future, a reliable and efficient solar energy storage system is key to maximizing the benefits of solar power.